

SASB: CG-MR-130a.1
UN SDGs: 7;13
TJX has made certain commitments to reduce the climate impacts of our own operations – meaning our stores, certain corporate offices, distribution (or processing) centers, and certain vehicles.1 To support our commitments, we work across our global business operations to measure, manage, and address these impacts.
Our global climate and energy targets include:
By 2030:
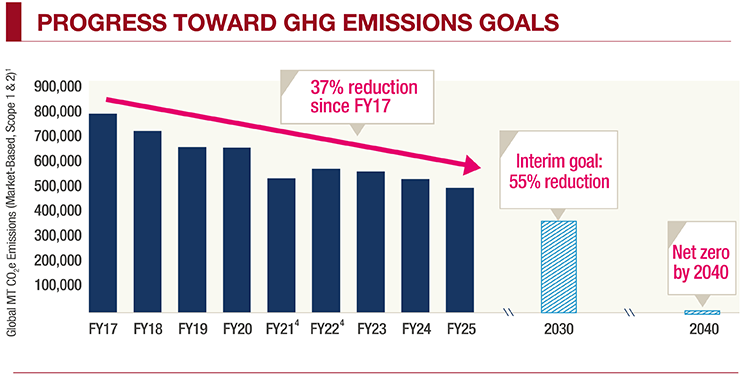
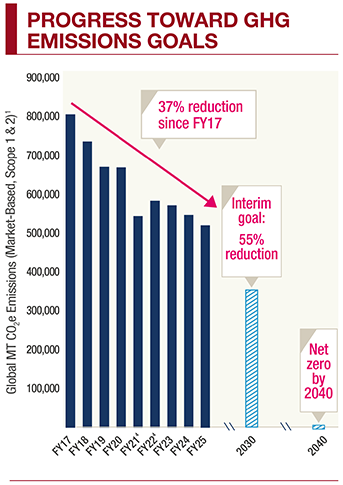
- We plan to achieve a 55% absolute reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from our own operations (Scope 1 and Scope 2) by Fiscal 2030 (against a Fiscal 2017 baseline).
We intend to source 100% renewable energy2 in our operations.
By 2040:
- We have a goal to achieve net zero GHG emissions in our own operations (Scope 1 and Scope 2).
These commitments were developed using industry guidance, research, and science-based models that support an emissions growth path aimed at limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, in line with the goals of the United Nations’ Paris Agreement.
TJX has an internal, cross-functional committee whose members are responsible for supporting the Company in making progress against our operational GHG and renewable energy targets and for contributing to the process for measuring and reporting key climate and energy data and metrics. Members of this committee lead the management and implementation of the Company’s net zero roadmap, which outlines our high-level plans and strategic approach to achieving our global climate and energy targets. Through this roadmap, we have identified strategies and tactics that aim to decrease our Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions in line with our commitments. These plans include a focus on reducing emissions in our facilities by investing in energy efficiency technologies, such as HVAC and LED lighting, as well as increasing renewable energy purchases. Our roadmap is dynamic, and we continue to monitor the development and feasibility of utilizing additional lower carbon technologies, such as electric vehicles and alternative fuels.
In Fiscal 2025, we estimate that our energy management and renewable and low-carbon energy sourcing efforts reduced our reported Scope 1 and Scope 2 (market-based) emissions by approximately 317,000 metric tons of CO2e.3
Progress Against Climate & Energy Goals
GHG Emissions:
We have achieved a 37% reduction in absolute, market-based GHG emissions from our Fiscal 2017 baseline.1 This represents approximately 67% of our Fiscal 2030 GHG emissions target achieved. We are progressing along our modeled emissions reduction pathway.
We reduced our absolute, market-based GHG emissions by 6.5% relative to Fiscal 2024. We continued to grow our business and operational footprint over the same period.
Renewable Energy:
40% of energy sourced for our own operations globally came from renewable sources.
In Fiscal 2025 alone, we sourced more than 715 million kilowatt hours of renewable and low-carbon energy.


Emissions in Our Own Operations
Energy Efficiency
Reducing energy consumption, where feasible, is one of our first considerations for decreasing emissions. Operations teams in each of our geographies are actively working to manage our energy consumption and costs, analyze and improve our operational performance, and test potential technologies in the facilities we operate to help us drive progress against our operational goals. Where feasible, we are taking the following steps:
- Implementing light-emitting diode (LED) technologies in stores and certain distribution centers globally
- Installing high-efficiency HVAC system upgrades in certain existing stores and distribution centers, including gas-to-electric HVAC system replacements in certain geographies
- Employing high-volume, low-speed (HVLS) fans in certain distribution centers and stores
- Installing and upgrading smart building management system (BMS) controls in certain geographies
- Utilizing energy-efficient building designs and controls in new buildings
- Exploring and leveraging utility-level energy efficiency incentives and programs
Where we are able, we are working to upgrade our stores globally to LED lighting. In Fiscal 2025, we again conducted more store retrofits than we conducted the year previously. The majority of our stores and distribution centers globally are now equipped with LED lighting technology.
In certain geographies, we also have been piloting and utilizing new technologies to help us optimize our energy usage through remote management, monitoring, and analysis of our energy systems and data.
Renewable & Low-Carbon Energy
We source low-carbon and renewable energy to help further reduce the GHG emissions associated with our electricity consumption. To work toward the achievement of our goal of sourcing 100% renewable energy in our global operations, we utilize a variety of renewable energy sourcing strategies. Some examples of our current sourcing strategies include:
- Wholesale off-site power purchase agreements
- On-site solar power purchase agreements
- Electricity supply contracts and utility green tariffs
- Unbundled energy attribute certificates (EACs)
We have deployed on-site solar at some of our U.S. distribution centers, including in Arizona, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Nevada, and Texas, as well as at our processing center in Australia. Because we lease, rather than own, nearly all our store locations, we have less flexibility in installing solar on store rooftops. That said, we have installed solar at select stores in both the U.S. and the U.K. We continue to engage in conversations with certain landlords to explore the feasibility of installing rooftop solar panels at additional locations.

TJX’s distribution center in El Paso,TX
features rooftop solar panels.
In Fiscal 2025,
40% of energy sourced for our own operations globally came from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind generation.
Our renewable and low-carbon energy sourcing strategies enabled us to reduce our Scope 2 market-based GHG emissions inventory by more than 300,000 metric tons of CO2e.3
- Compared to Fiscal 2024, TJX purchased more than 160,000 megawatt hours more renewable and low-carbon energy.
Transportation & Fuel (Scope 1)
Our Scope 1 emissions include emissions from the use of natural gas, diesel, and other fuel sources within our own operations. To help address these emissions, we are monitoring the development of, and in limited instances have begun deploying, alternative fuel or electric vehicles as well as electric building heating and cooling systems.
Although TJX does not generally own or lease the vehicles that transport our merchandise, some vehicles do fall within our operational footprint (Scope 1) in limited instances. This includes where we directly manage our logistics and distribution for long-haul and outbound store deliveries, such as in the U.K. and Ireland, as well as some fleet vehicles. Together with our partners, we work to simultaneously increase fuel efficiency, lower costs, and reduce emissions where feasible. Our key strategies for reducing these Scope 1 emissions include:
In the U.S. we:
- Offer hybrid electric company vehicles to eligible Associates in the field and utilize hybrid cars for a portion of our fleet vehicles
- Utilize battery-powered forklifts in our distribution centers
In the U.K. and Ireland, TJX Europe has:
- Continued to utilize longer semi trailers, which improves efficiency by increasing average payload
- Begun utilizing a limited number of biogenic compressed natural gas (bio-CNG) tractor-trailer trucks for outbound deliveries to stores. In Fiscal 2025, TJX Europe also utilized some trucks that were powered primarily by liquified biomethane (bio-LNG).
- Adopted a fuel efficiency driver training program as part of its driver development process
- Supported ongoing initiatives including the implementation of fleet analytics and tire pressure monitoring to deliver incremental fuel efficiency as well as regularly reviewing its delivery schedules to reduce miles traveled and empty miles

We also continue to monitor the development and deployment of technologies that could help us reduce Scope 1 emissions in our owned and leased buildings. For example, when looking to upgrade HVAC systems, we may consider the use of more efficient HVAC technologies, and in certain geographies we are beginning to pilot the use of electric heat pumps.
Building Green
Where feasible when we construct new buildings and in buildings where we have more control, we have worked to incorporate features that support our environmental sustainability efforts. For example, we aim for our newly constructed distribution centers and processing centers to be able to accommodate on-site solar arrays wherever feasible. Furthermore, when we move into existing properties, as part of the renovation process, our design teams typically consider ways to improve energy efficiency and water conservation and to develop waste sortation and recycling infrastructure. We also have installed electric vehicle charging stations at certain locations across our geographies.

Integrating Sustainability Into Operations
Green Certified Buildings (LEED, BREEAM, Green Star):
- Phoenix, AZ, U.S.
- Jefferson, GA, U.S.
- Marlborough, MA, U.S.
- Las Vegas, NV, U.S.
- New Albany, OH, U.S.
- Mississauga, ON, Canada
- Balham, U.K.
- Didcot, U.K.
- Hackney, U.K.
- Hereford, U.K.
- Watford, U.K.
- Sulechów, Poland
- Marsden Park, NSW, Australia
On-Site Solar Installations*:
- Phoenix, AZ, , U.S.
- Tucson, AZ, U.S.
- Clovis, CA, U.S.
- Dublin, CA, U.S.
- El Segondo, CA, U.S.
- Oxnard, CA, U.S.
- Palmdale, CA, U.S.
- Paso Robles, CA, U.S.
- Petaluma, CA, U.S.
- Rowland Heights, CA, U.S.
- San Diego, CA, U.S. (x2)
- San Dimas, CA, U.S.
- Torrance, CA, U.S.
- Vallejo, CA, U.S.
- Bristol, CT, U.S.
- Norwell, MA, U.S.
- Worcester, MA, U.S.
- Brick, NJ, U.S.
- Bridgewater, NJ, U.S.
- Edgewater, NJ, U.S.
- Holmdel, NJ, U.S.
- North Brunswick, NJ
- Secaucus, NJ, U.S. (x2)
- N Las Vegas, NV, U.S.
- Westbury, NY, U.S. (x2)
- El Paso, TX, U.S.
- Banbury, U.K.
- Barnsley, U.K.
- Altringcham, U.K.
- Stevenage, U.K
- Marsden Park, NSW, Australia
Off-Site Renewable or Carbon-Free Product:
- Colorado, U.S.
- Connecticut, U.S.
- Illinois, U.S.
- Massachusetts, U.S.
- New York, U.S.
- Alberta, Canada
- Nova Scotia, Canada
- Saskatchewan, Canada
EV Charging Installations:
- Framingham, MA, U.S.
- Mississauga, ON, Canada
- Brampton, ON, Canada
- Watford, U.K.
- Bergheim, Germany
*In some cases, TJX chooses not to retain ownership to the energy attribute certificates associated with the installation.

Green Certified Buildings (LEED, BREEAM, Green Star):
- Phoenix, AZ, U.S.
- Jefferson, GA, U.S.
- Marlborough, MA, U.S.
- Las Vegas, NV, U.S.
- New Albany, OH, U.S.
- Mississauga, ON, Canada
- Balham, U.K.
- Didcot, U.K.
- Hackney, U.K.
- Hereford, U.K.
- Watford, U.K.
- Sulechów, Poland
- Marsden Park, NSW, Australia
On-Site Solar Installations*:
- Phoenix, AZ, , U.S.
- Tucson, AZ, U.S.
- Clovis, CA, U.S.
- Dublin, CA, U.S.
- El Segondo, CA, U.S.
- Oxnard, CA, U.S.
- Palmdale, CA, U.S.
- Paso Robles, CA, U.S.
- Petaluma, CA, U.S.
- Rowland Heights, CA, U.S.
- San Diego, CA, U.S. (x2)
- San Dimas, CA, U.S.
- Torrance, CA, U.S.
- Vallejo, CA, U.S.
- Bristol, CT, U.S.
- Norwell, MA, U.S.
- Worcester, MA, U.S.
- Brick, NJ, U.S.
- Bridgewater, NJ, U.S.
- Edgewater, NJ, U.S.
- Holmdel, NJ, U.S.
- North Brunswick, NJ
- Secaucus, NJ, U.S. (x2)
- N Las Vegas, NV, U.S.
- Westbury, NY, U.S. (x2)
- El Paso, TX, U.S.
- Banbury, U.K.
- Barnsley, U.K.
- Altringcham, U.K.
- Stevenage, U.K
- Marsden Park, NSW, Australia
Off-Site Renewable or Carbon-Free Product:
- Colorado, U.S.
- Connecticut, U.S.
- Illinois, U.S.
- Massachusetts, U.S.
- New York, U.S.
- Alberta, Canada
- Nova Scotia, Canada
- Saskatchewan, Canada
EV Charging Installations:
- Framingham, MA, U.S.
- Mississauga, ON, Canada
- Brampton, ON, Canada
- Watford, U.K.
- Bergheim, Germany
*In some cases, TJX chooses not to retain ownership to the energy attribute certificates associated with the installation.
Emissions in Our Value Chain
Estimating Scope 3 Emissions
We continue to work toward improving our Scope 3 emissions estimations as we prepare for a variety of anticipated regulatory disclosures.
As an off-price retailer, our opportunistic and flexible buying strategy is to acquire a rapidly changing assortment of merchandise in a variety of ways on an ongoing basis and close to need from an expansive universe of merchandise vendors. This means that both our overall vendor base and product mix can change frequently as we work to offer our customers an ever-changing, treasure hunt shopping experience. In addition, we do not own, operate, or control the facilities that manufacture products sold in our stores. These various aspects of our business model make Scope 3 emissions estimations particularly complex and challenging.
Despite these complexities, we have continued to work to better understand our emissions from Scope 3 categories. For example, we evaluated all 15 Scope 3 emissions categories, both upstream and downstream, and developed order of magnitude estimates of relevant categories using a variety of methodologies, including economic input-output lifecycle assessment (EIO-LCA). This provided us with a better understanding of emissions hotspots in our value chain and identified that our largest category of Scope 3 emissions is purchased goods and services (Scope 3, Category 1). Other relevant categories of Scope 3 emissions that were identified include upstream transportation and distribution (Scope 3, Category 4) and use of sold products (Scope 3, Category 11).
We also have looked across the organization to find and collect data from vendors and internal systems that could be used to support calculation and estimation of relevant Scope 3 categories. For example, we have access to activity data related to business travel (Scope 3, Category 6) and waste generated in our operations (Scope 3, Category 5), and we worked with our e-commerce fulfillment providers to get access to data regarding downstream transportation and distribution (Scope 3, Category 9). We have reported on our Scope 3 emissions for these three categories for several years.
We are taking steps to establish processes to standardize the estimation of relevant Scope 3 categories. We expect that these processes will continue to rely on EIO-LCA and other methodologies that rely on economy- or industry-wide emissions intensities in the estimation of some of our largest emissions categories.
Some additional steps we have begun to take to better understand our Scope 3 emissions include:
Education. We participate in industry associations and groups, such as the Textile Exchange, which provide us with an opportunity to learn from others.
Partnerships. We have begun engaging with certain logistics carriers to develop an understanding of any emissions reduction strategies or initiatives.
Mining our data. Given the challenges of our business model as it relates to Scope 3, we have begun to examine our own data to determine activity data sources that could support our work in this space. We have started this work by focusing where we have access to the most data, including products for which we have more control in bringing to market. While this is very early stage, an initial test with one material type provided us with insight that we believe may help us better estimate emissions across the entirety of that material type, regardless of how we source it.
Leveraging external resources. We are working with a technology partner to support our emissions calculations, including Scope 3.
Transportation & Fuel (Scope 3)
Our logistics teams worldwide seek out strategies and solutions that can help us increase the efficiency of our logistics and transportation operations and reduce fuel used to transport our merchandise throughout our distribution network. We strive to conserve fuel, reduce travel time, and decrease the number of trucks on the road. We use a variety of tactics and technologies to support our efficiency and fuel conservation initiatives; this may include, for example, using modeling software to improve the efficiency of our store delivery network, increasing the utilization of trailer space, and testing new alternative fuel vehicles.
Where feasible and when aligned with our business, we use rail and intermodal5 for moving merchandise throughout our network. This is generally more fuel efficient and produces fewer emissions than trucking alone. We estimate that in Fiscal 2025, rail and intermodal shipping resulted in approximately 430,000 fewer metric tons of CO2e emissions than shipping the same volume by truck only.
In the U.S., where practicable, we utilize intermodal, centrally located service centers, and strategic partnerships to help increase the efficiency of our distribution network.
Our service centers, which are smaller than distribution centers, are located closer to store clusters and are designed to improve the efficiency of our store delivery process. We also utilize these service centers to co-locate our Asset Recovery & Recycling Centers (ARRCs). ARRCs enable us to maximize our delivery trucks’ utilization by backhauling re-usable and recyclable materials. Learn more about the value our ARRC network brings to our business in the Waste Management section of our website.
- We engage directly with our logistics partners and indirectly through third parties (such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) SmartWay® Transport Partnership) to identify potential opportunities that may result in emissions reductions.
- TJX requires that all new U.S. carriers are EPA SmartWay-certified and has collaborated with existing carriers to encourage their participation in the program. In Calendar Year 2024, 100% of TJX’s U.S. freight and logistics ton-mileage was with SmartWay-certified carriers. TJX was recognized as a SmartWay High Performer in 2024 and was also awarded a 2024 SmartWay Excellence Award, which recognizes partners for their environmental performance and freight sustainability leadership.
- We have been trialing the use of electric vehicles (EVs) in certain distribution centers for yard moves.
- We continue to explore innovative opportunities for improving freight efficiency through leveraging new technologies and enhancing our processes.


Additionally, we have begun to consider ways we can support home office and certain distribution center Associates who wish to commute to work in a more emissions-friendly manner. For example, we offer EV charging at our home offices in Canada, the U.K., and certain locations in the U.S., as well as at certain processing centers in Europe and Australia. In the U.S., we also organize carpool programs and provide regular shuttles between our Massachusetts home office locations and the local commuter train station.
Additional Environmental Sustainability Initiatives
In recent years, teams around the business have undertaken various environmental sustainability initiatives that also contribute to helping support local ecosystems around the world. Some examples include:
- TK Maxx in the U.K. has been a partner of the Woodland Trust for more than 20 years. The Woodland Trust is the U.K.’s largest woodland conservation charity with an aim to play a central role in protecting, restoring, and creating woodlands to benefit people, wildlife, and the environment. Since the partnership began, TK Maxx and its customers have helped the Woodland Trust plant over 80,000 trees.
- TJX has worked with local companies to install beehives at our office locations in both Framingham, Massachusetts and Watford, England. These programs engage our Associates at these office locations, while also aiming to support plant health and biodiversity in the surrounding local areas.
- TJX Canada recently partnered with Veritree to help restore critical landscapes around the world through verifiable tree plantings. With the support of this partnership, nearly 40,000 trees were planted across parts of Canada and Haiti.
Where feasible and available in the marketplace, we have sourced certain products that contain paper, paperboard, and wood materials that have undergone Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification, such as FSC-certified wood for some outdoor furniture sold at our HomeGoods stores and FSC-certified paper stock for certain stationery, gift wrap, and gift card styles sold across our stores globally. Learn more about our FSC sourcing on the Sustainable Sourcing page of our website.


Sustainable Sourcing
We continue to work on initiatives related to sourcing certain products, product packaging, and operational supplies with sustainable attributes, primarily focused on areas where we have more control.
Learn moreSustainable Sourcing
We continue to work on initiatives related to sourcing certain products, product packaging, and operational supplies with sustainable attributes, primarily focused on areas where we have more control.
Learn moreClimate Data Reporting & Third-Party Assurance
TJX has engaged an independent third party to provide limited assurance on a portion of our GHG emissions data since Fiscal 2015.
- TJX has received third-party limited assurance over our global Scope 1 and Scope 2 (location- and market-based) emissions data for our Fiscal 2025 reporting period, in accordance with AIPCA attestation standards (AT-C 105 and AT-C 210).
- We also received third-party limited assurance over approximately 76% of our global Scope 3, Category 6 (Business Travel) and all of our global Scope 3, Category 9 (Downstream Transportation and Distribution) emissions data for our Fiscal 2025 reporting period, in accordance with AICPA attestation standards (AT-C 105 and AT-C 210).
To learn more about our environmental sustainability data and reporting, and to access our response to the latest CDP Climate Change Questionnaire, visit our Reporting & Disclosures page.
Spotlight



Spotlight:
Engaging Associates in Support of the Environment
In addition to engaging Associates in nonprofit giving through Associate-Nominated Grants, which can be read about in the Communities section, TJX Europe has invited Associates to participate in its nonprofit giving specific to environmental sustainability. This giving is done with donations made from the Environment Fund, which is funded by the sale of certain reusable carryout bags.
For the proceeds of Fiscal 2025 sales of these bags, TJX Europe organized an Associate vote, whereby Associates in each of our major European markets were able to vote for their favorite nonprofit from a list of organizations that work in nature conservation, biodiversity, climate change, and/or waste reduction. Funding amounts were decided based on voting results. Some of the organizations that received funding included Stichting Boomfeestdag in the Netherlands, which engages in tree planting to help foster environmental stewardship; Deutsche Wildtier Stiftung in Germany, which aims to protect and restore forest ecosystems; and Marine Conservation Society in the U.K., which aims to empower communities to combat beach pollution and foster ocean literacy.
1Excludes GHG emissions from cooling and certain heating and refrigerant sources used by certain locations where TJX was not billed directly for our usage.
2Electricity only.
3TJX calculates the reduction in Scope 2, market-based emissions due to renewable and low carbon energy sourcing as follows: renewable and low carbon energy purchases (MWh) multiplied by the relevant market-based emissions factors (MT CO2e/MWh) that would have been applied in the absence of renewable energy purchases.
4Fiscal 2021 and 2022 reductions were impacted by store closures due to the COVID-19 global pandemic.
5Transportation involving more than one form of carrier during a single journey.
Updated September 2025